Company name and address:
| modas mobile Datensysteme GmbH | ||||||||||
| Belziger Str. 69-71 | ||||||||||
| D-10823 Berlin | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Location: Berlin, Germany / Amtsgericht Berlin Charlottenburg HRB 56053 | ||||||||||
| Executive directors: Werner Marquardt, Günter Rohgengel |
Disclaimer
modas reserves the right not to be responsible for the topicality, correctness, completeness or quality of the information provided. Liability claims regarding damage caused by the use of any information provided, including any kind of information which is incomplete or incorrect, will therefore be rejected.
All offers are not-binding and without obligation. Parts of the pages or the complete publication including all offers and information might be extended, changed or partly or completely deleted by the author without separate announcement.
Copyright
The author is intended not to use any copyrighted material for the publication or, if not possible, to indicate the copyright of the respective object. The copyright for any material created by the author is reserved. Any duplication or use of objects such as images, diagrams, sounds or texts in other electronic or printed publications is not permitted without the author's agreement.
Privacy policy
If the opportunity for the input of personal or business data (email addresses, name, addresses) is given, the input of these data takes place voluntarily. The use and payment of all offered services are permitted - if and so far technically possible and reasonable - without specification of any personal data or under specification of anonymized data or an alias. The use of published postal addresses, telephone or fax numbers and email addresses for marketing purposes is prohibited, offenders sending unwanted spam messages will be punished.
Distribution
If you are interested in the products of ![]() visit our Online Shop.
visit our Online Shop.
If you have any questions, do not hesitate to contact us:
Herr Dipl. Ing. Günter Rohgengel
Phone: +49 30 230973 37
E-Mail:
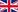
WLAN Client Products
The MC-WLAN-Client-Adapter family provides devices with an Ethernet interface the ability to communicate wirelessly over an existing wireless network. Serial communicating client devices can be connected to a WLAN infrastructure via the serial interface of the MC-Adapter.All necessary parameters to establish the wireless connection is maintained in the MC-WLAN-Client-Adapters so the LAN client don't need additional drivers or configuration effort to use the wireless network. The typical application for the MC adapter is the broad field of machine-to-machine communication via WLAN infrastructures. These include mobile installations such as forklifter or AGVs.
The presented 3 MC-Adapter, all based on the same processor platform and vary only in the different available interfaces.
|
|
Device Properties:
Hardware:
- Processor Board with ARM® Cortex®-A9 Core
- Memory: 128MByte DDR-RAM and 4GB Flash
- 802.11a/b/g/n for 2.4 + 5 GHz WLAN, Data Rates up to 300 Mbit/s
- 1,2 or 4 Gigabit LAN Port
- RS232 Serial Port
- USB2-Port, also for port extension
- 1 x Relay
- 1 x Digital Input
- Power Supply 10-60V or via PoE (LAN)
- Robust aluminium housing with different mounting options
- Largely compatible (mechanically and functionally) with previous models WLX and ESCG.
Features:
- Configuration via website (HTTP or HTTPS), REST-API or the MCConfig-Application
- SNMP Monitoring
- Different Bridge-Modes for LAN-Client-Connections: (Bridge Modes)
- NAT
- Single Client NAT
- Single Client Cloning
- Level 2 Bridge
- MWLC Mode (Tunning LAN-Client data traffic to stationary network)
- Certificate Management for 802.1x authentication (WPA2 Enterprise)
- SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol)
- 802.11r Fast-Roaming
- 802.11k Radio Resource Management
- 802.11e Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service (WMM QoS)
Technical Info
| Datasheets | MC1 | MC2 | MC4 |
| Features |
Specifications |
| Ethernet | 1,2 or 4 x 10/100/1000 MBit Auto MDI/MDIX |
| Serial | 1 x RS232, 300-460.8 KBit/s, RTS, CTS, DSR, DTR or (RS422,RS485) (MC1+MC2) |
| USB | 1 x USB2 for connecting printers or USB-Adapters with different other ports |
| Relay | 1 x Switch, max 1A@24V, max 125VAC |
| Signal Input | 1 x galvanically isolated 10-72V |
| Antenna Connectors | 2 x RPSMA (optional TNC or RPTNC) |
| Power Supply | 10-60VDC or 802.3af PoE via LAN Port |
| Energy | <= 5W (typically 3.5W) |
| Temperature | 0-60°C |
| Dimensions | 105x125x35mm |
| Weight | ca. 400g |
Wireless LAN Interface
| Technology | 802.11 a/b/g/n WLAN (2.4 + 5 GHz band) | ||||||||||
| Antennas | 2 Antennas (2T2R MIMO) | ||||||||||
| Encryption | WEP (64, 128bit) + TKIP/AES | ||||||||||
| Security |
802.11i WPA(2) - PSK |
||||||||||
| Channels |
802.11b/g/n ETSI 1-13, USA/Canada 1-11 |
||||||||||
| Data Rates |
|
||||||||||
| Transmission Power |
802.11b/g 17 dBm |
Order Codes:
| Option | Order Code | MC-Adapter |
| Housing with mounting tabs | MCn-SL... | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| Housing with DIN-Rail-Clip | MCn-SC... | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| M12 Connector | MCn-Sx-M12 | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| 8 PIN Weidmüller Terminal Block | MCn-Sx-WK8 | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| M8 Connector | MCn-Sx-M8 | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| Relay | MCn-Sx-xx-REL | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| Signal Input | MCn-Sx-xx-INP | MC1, MC2 |
| Serial Interface RS485 | MCn-Sx-xx-RS485 | MC1, MC2 |
| Serial Interface RS422 | MCn-Sx-xx-RS422 | MC1, MC2 |
| TNC Antenna Connector | MCn-Sx-xx-1(2)TNC | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
| RPTNC Antenna Connector | MCn-Sx-xx-1(2)RTNC | MC1, MC2, MC4 |
Typical configurations for the use of the MC wireless client adapter
The MC WLAN-Client-Adapter is used to connect one or more devices with an Ethernet interface via a WLAN infrastructure to a stationary network.
The MC offers various bridge modes to meet application-specific requirements
| Bridge mode | LAN-Clients | IP's im WLAN | Transparency | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAN Client Cloning | 1 | 1 (LAN Client IP) | all ports | IP- and MAC-address of the LAN-Client is registered in the WLAN. |
| Single Client NAT | 1 | 1 (MC IP) | all ports |
IP- and WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
| NAT | as many | 1 (MC IP) | Ports def. by config |
IP- and WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
| Level 2 Bridge | as many | n LAN-Clients + 1 | all ports | All LAN-Client-IP's and the MC-IP are registered with the WLAN-MAC-address of the MC. |
| MWLC-Mode | as many | 1 (MC IP) | all ports |
Only the IP- and the WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
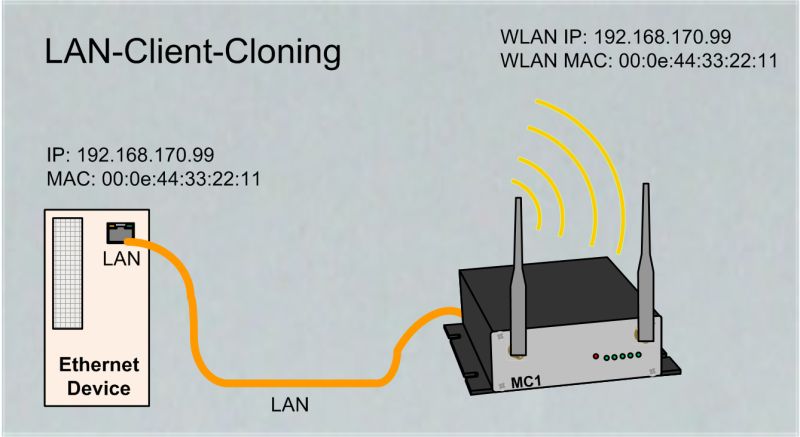
LAN Client Cloning Mode
|
In this mode the device connected to the LAN port of the MC determines the IP- and the MAC-address of the WLAN connection that the MC establish to the WLAN infrastructure. The configuration and monitoring of the MC is done via the IP address of the LAN-Client. |
|
If only one LAN client is connected to the MC, this mode should be preferred. |
|
|
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
NAT- and Single-NAT Mode
The NAT mode is characterized in that the LAN clients connected to the MC work in a separate network from the wireless network. The traffic of the LAN clients via WLAN to the stationary network is transformed by the MC, so that all data is sent and received via the IP address of the MC.
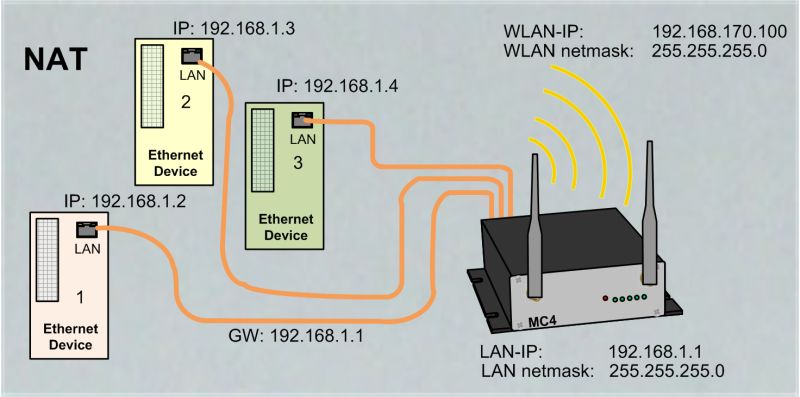 |
What to consider: If multiple LAN clients are connected to the MC the NAT mode must be defined. |
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
Level 2 Pseudo-Bridge Mode
In this mode, each LAN client communicates with its own IP address over the wireless network. However, all data is sent with the MAC address of the MC-WLAN card. This procedure can make problems in some WLAN infrastructure systems. Problems can appear when the WLAN controller is working with ARP caching.
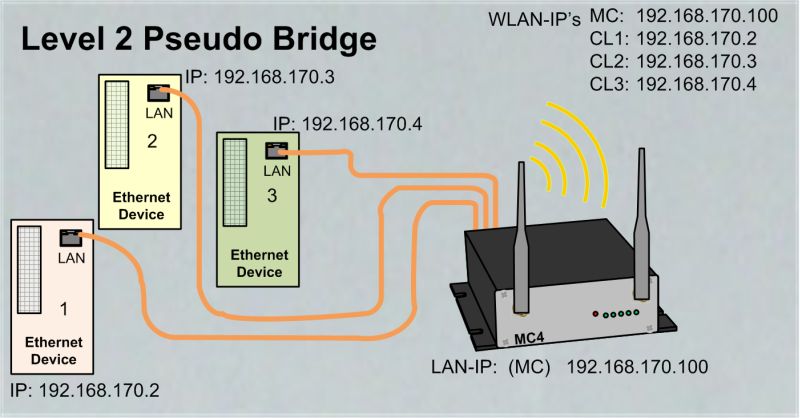 |
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
MWLC-Mode
|
With the MWLC mode, all restrictions on the availability, IP address assignment and transparency especially in applications with multiple LAN clients are solved. In this Mode all data packets received from the LAN-Clients are tunneled by the MC (Slave) to another MC (master) that is installed on stationary network side. The master MC extract the LAN-Client data packets and send it into the stationary network. |
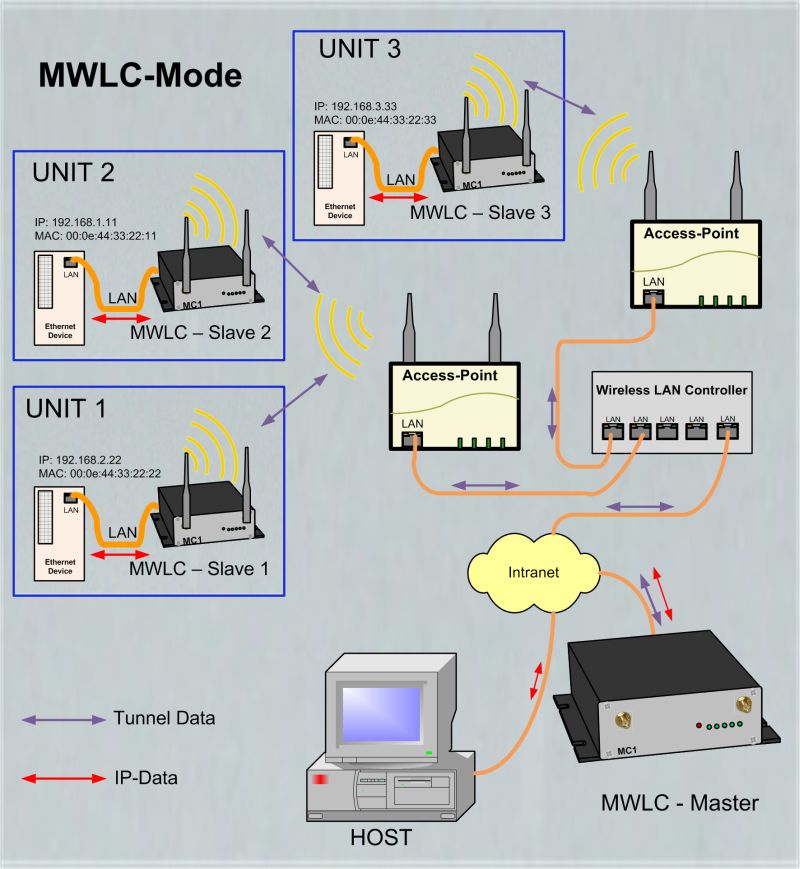 |
|
In this mode the IP addresses of the LAN clients has no influence to the MC. The LAN-Clients are connected to the stationary network with there own IP- and MAC addresses. Because the MWLC master in this constellation plays a central role, and a failure of this device would disconnect all clients, there is the possibility to install a 2nd MWLC master as a backup. |
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
For a more detailed description of these modes, refer to the MC Manual.
Wireless connection of a device with a serial interface
Serial port to network connectionThe MC wireless adapter can be used to connect a device with a serial interface via WLAN with an application that runs on a control computer. The communication between the application and the device at the MC can be done via the following protocols:
|
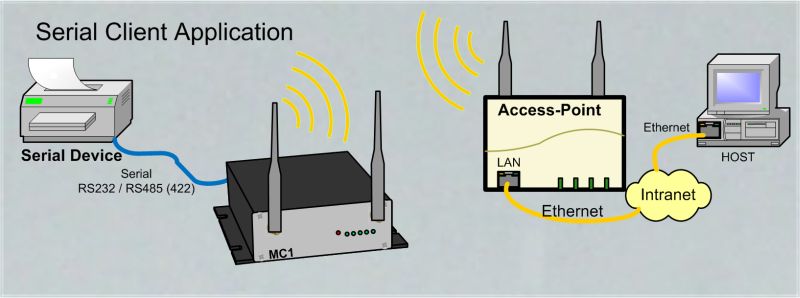 |
Port to Port ConnectionIf the user want's to connect 2 devices via there serial interfaces it can be done with 2 MC. The serial data between the 2 serial interfaces can be exchanged via LAN or WLAN in a WLAN infrastructure or in Adhoc mode constellation. |
|
The used protocol between the 2 serial devices should not have high real-time requirements. |
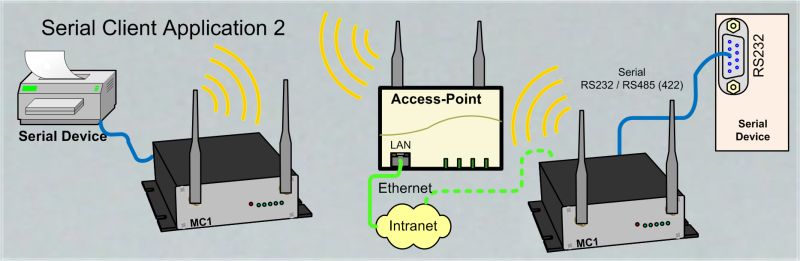 |
| The MC can be used at the same time as a serial and an Ethernet client. |