Typical configurations for the use of the MC wireless client adapter
The MC WLAN-Client-Adapter is used to connect one or more devices with an Ethernet interface via a WLAN infrastructure to a stationary network.
The MC offers various bridge modes to meet application-specific requirements
| Bridge mode | LAN-Clients | IP's im WLAN | Transparency | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAN Client Cloning | 1 | 1 (LAN Client IP) | all ports | IP- and MAC-address of the LAN-Client is registered in the WLAN. |
| Single Client NAT | 1 | 1 (MC IP) | all ports |
IP- and WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
| NAT | as many | 1 (MC IP) | Ports def. by config |
IP- and WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
| Level 2 Bridge | as many | n LAN-Clients + 1 | all ports | All LAN-Client-IP's and the MC-IP are registered with the WLAN-MAC-address of the MC. |
| MWLC-Mode | as many | 1 (MC IP) | all ports |
Only the IP- and the WLAN-MAC-address of the MC is registered in the WLAN. |
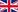
LAN Client Cloning Mode
|
In this mode the device connected to the LAN port of the MC determines the IP- and the MAC-address of the WLAN connection that the MC establish to the WLAN infrastructure. The configuration and monitoring of the MC is done via the IP address of the LAN-Client. |
|
If only one LAN client is connected to the MC, this mode should be preferred. |
|
|
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
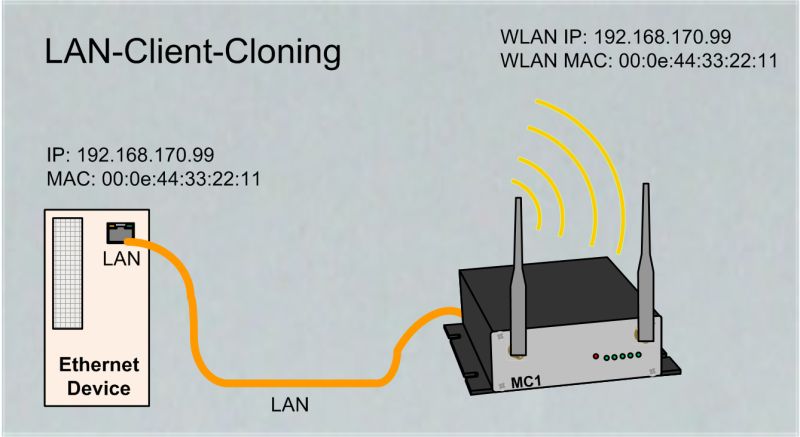
NAT- and Single-NAT Mode
The NAT mode is characterized in that the LAN clients connected to the MC work in a separate network from the wireless network. The traffic of the LAN clients via WLAN to the stationary network is transformed by the MC, so that all data is sent and received via the IP address of the MC.
 |
What to consider: If multiple LAN clients are connected to the MC the NAT mode must be defined. |
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
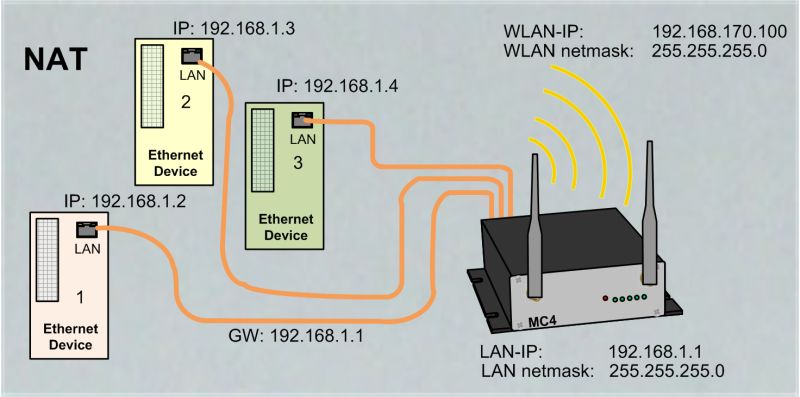
Level 2 Pseudo-Bridge Mode
In this mode, each LAN client communicates with its own IP address over the wireless network. However, all data is sent with the MAC address of the MC-WLAN card. This procedure can make problems in some WLAN infrastructure systems. Problems can appear when the WLAN controller is working with ARP caching.
 |
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
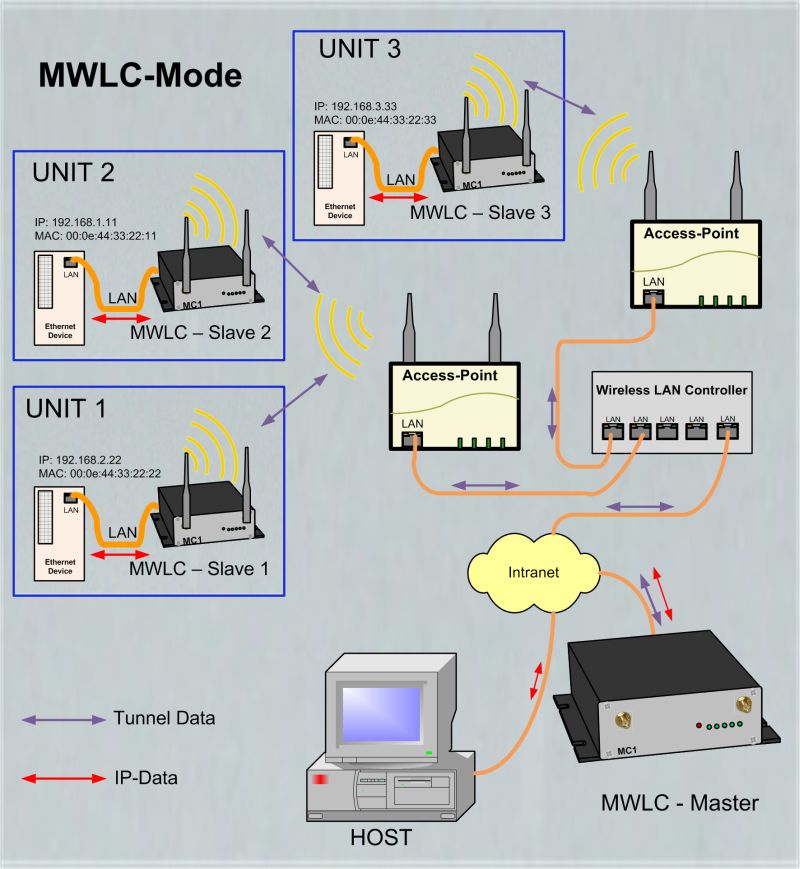
MWLC-Mode
|
With the MWLC mode, all restrictions on the availability, IP address assignment and transparency especially in applications with multiple LAN clients are solved. In this Mode all data packets received from the LAN-Clients are tunneled by the MC (Slave) to another MC (master) that is installed on stationary network side. The master MC extract the LAN-Client data packets and send it into the stationary network. |
 |
|
In this mode the IP addresses of the LAN clients has no influence to the MC. The LAN-Clients are connected to the stationary network with there own IP- and MAC addresses. Because the MWLC master in this constellation plays a central role, and a failure of this device would disconnect all clients, there is the possibility to install a 2nd MWLC master as a backup. |
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
For a more detailed description of these modes, refer to the MC Manual.